High-capacity steel warehouses are a core component of modern logistics, manufacturing, and distribution networks. As supply chains scale up and inventory volumes increase, warehouse buildings must support heavier loads, wider spans, taller storage systems, and highly efficient material flows. Achieving these objectives requires more than simply increasing building size—it demands a disciplined approach to structural and functional design.
High capacity steel warehouse design focuses on optimizing load-bearing performance, spatial efficiency, and long-term operational reliability. From span width and column layout to racking load capacity and future expansion potential, every design decision directly affects warehouse performance and lifecycle cost.
This article outlines the key design principles for high-capacity steel warehouses, helping developers, engineers, and operators create facilities that maximize storage density while maintaining safety, flexibility, and cost efficiency.
Understanding High-Capacity Steel Warehouse Requirements
A high-capacity steel warehouse is defined by its ability to accommodate large storage volumes and heavy operational loads within a clear, unobstructed space. Unlike conventional warehouses, these facilities often support:
- High-bay racking systems
- Automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS)
- Heavy pallet loads or bulk materials
- High forklift traffic and material handling equipment
Effective high capacity steel warehouse design begins with a clear understanding of operational needs, including storage density targets, material types, handling methods, and future scalability.
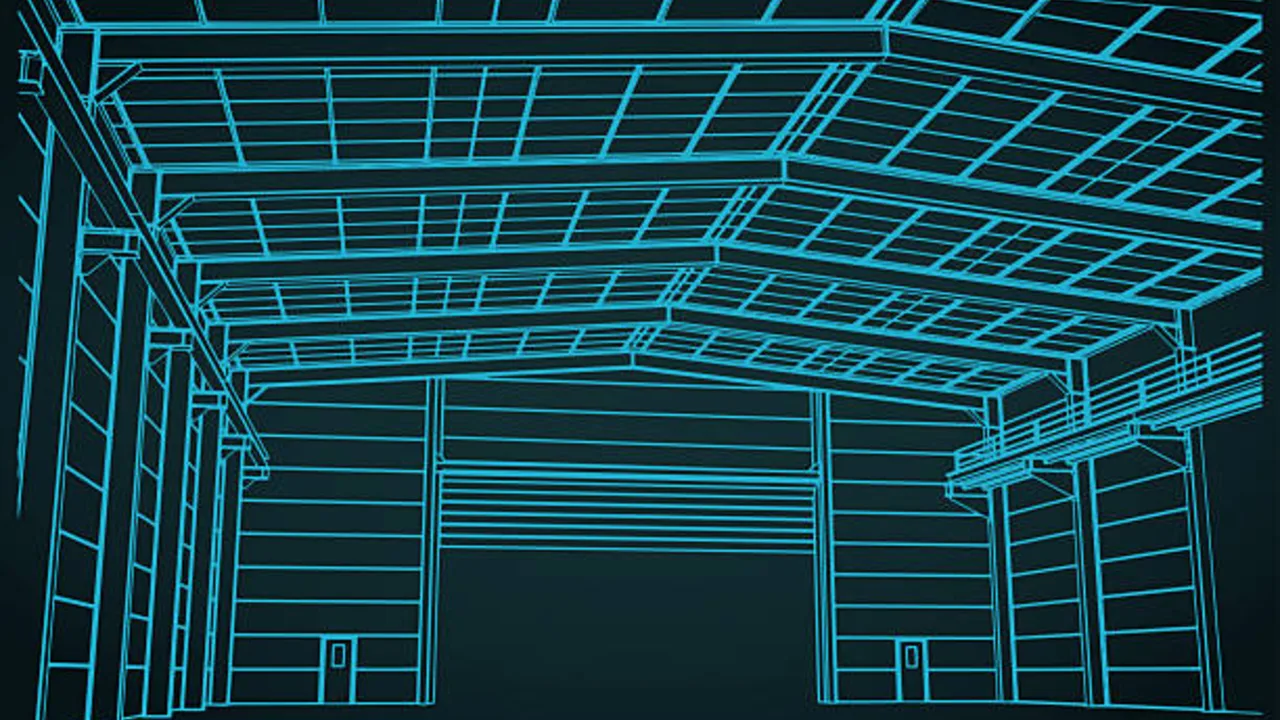
Structural System Selection
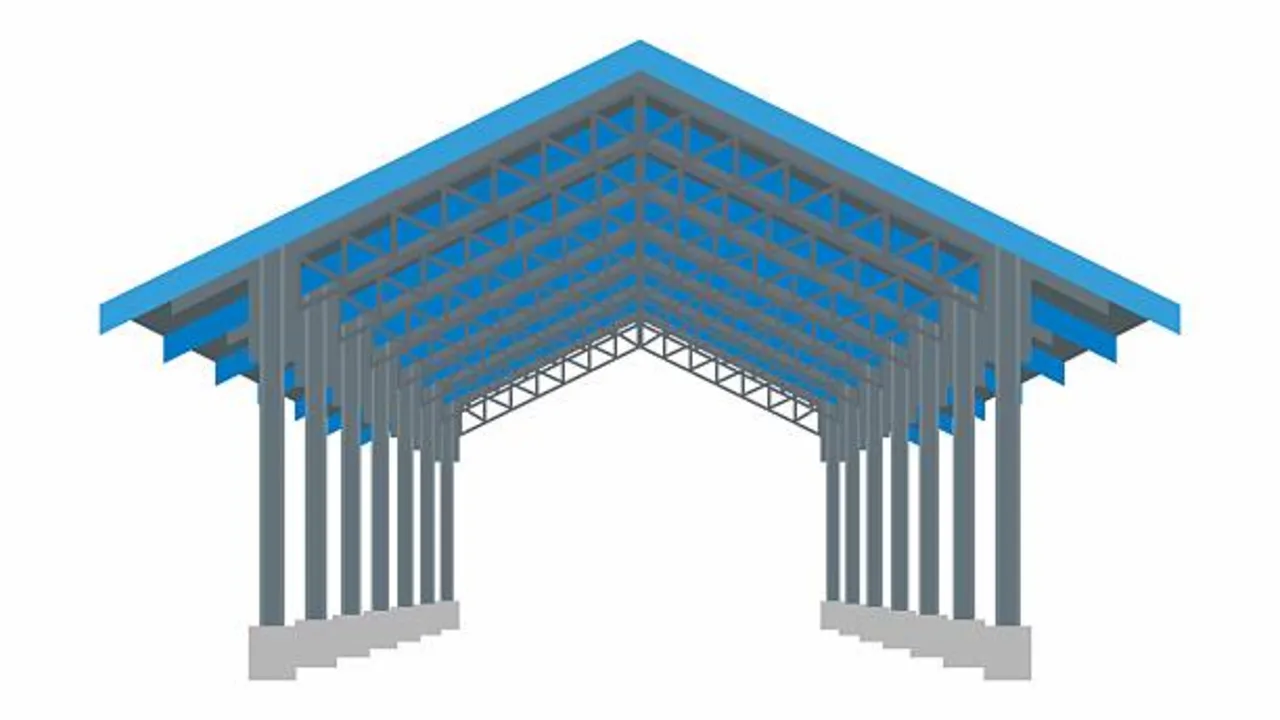
The choice of structural system forms the foundation of warehouse performance and directly influences load capacity, spatial efficiency, construction speed, and long-term operating costs. In high-capacity facilities, the structural system must not only support heavy vertical and lateral loads but also maintain large unobstructed interior spaces that maximize storage density and material handling efficiency.
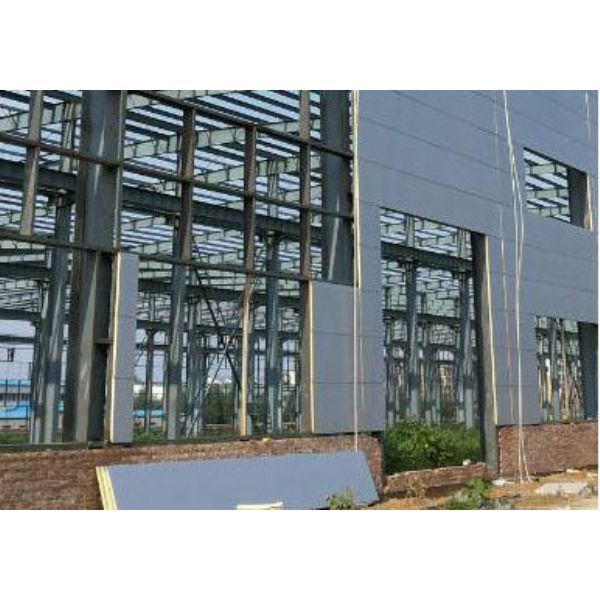
Steel structures are preferred for high-capacity warehouses because of their high strength-to-weight ratio, modular construction approach, and flexibility in accommodating long spans and tall clear heights. Compared with concrete systems, steel framing allows faster erection, easier future modification, and more precise control of structural behavior under heavy racking and equipment loads.
Common structural systems used in high-capacity steel warehouses include:
- Portal rigid frame systems
Portal frames are widely used due to their structural efficiency and cost-effectiveness. They provide large clear spans with minimal internal columns, making them ideal for racking-intensive layouts. Portal frames are especially suitable for medium to large warehouses where clear floor space and rapid construction are priorities. - Truss-supported roof systems
Truss systems are often applied when very wide spans or high roof loads are required. By distributing forces efficiently, roof trusses reduce bending moments in primary members and allow for longer spans without excessive steel tonnage. Truss-supported systems are commonly used in warehouses with heavy roof-mounted equipment, cranes, or extensive daylighting requirements. - Multi-span steel frames with optimized column grids
In extremely large facilities, multi-span frames with carefully planned column grids can provide a balance between structural economy and operational efficiency. By aligning columns with racking layouts and traffic lanes, designers can reduce steel weight while maintaining high storage capacity and flexible circulation patterns.
The selected structural system must balance structural efficiency with construction cost and operational flexibility. Overdesigned systems can unnecessarily increase steel tonnage and project cost, while underdesigned systems may limit future capacity expansion or compromise safety. An integrated design approach—coordinating structural engineering, warehouse operations, and racking systems—ensures that the chosen system delivers both high load performance and long-term adaptability.
Span Width and Clear Space Optimization
Span width is one of the most critical factors in warehouse design. Wider spans reduce the number of internal columns, creating uninterrupted floor space that improves racking layout and material flow.
Key considerations for span width include:
- Racking aisle configuration
- Forklift turning radius and traffic patterns
- Compatibility with automation systems
- Structural deflection control
While wider spans increase structural demands, optimized steel framing can achieve large clear spans without excessive material usage when properly engineered.
Racking Load and Floor Load Design
Racking load directly influences both superstructure and foundation design. High-capacity warehouses often support concentrated loads from tall racking systems that transfer forces to the floor slab and foundations.
Design considerations include:
- Maximum pallet weight and stacking height
- Rack-supported vs. free-standing racking systems
- Dynamic loads from forklifts or automated systems
- Load distribution and impact factors
Close coordination between structural engineers and racking suppliers is essential to ensure that racking loads are safely integrated into the building design.
Vertical Space Utilization and Clear Height
Maximizing vertical storage is a defining feature of high-capacity warehouses. Clear height must be sufficient to support high-bay racking while maintaining safe clearances for handling equipment and fire protection systems.
Key vertical design factors include:
- Clear internal height below roof structure
- Roof slope and truss depth
- Integration of lighting, sprinklers, and ventilation
- Future racking height increases
Steel structures allow efficient vertical design with minimal structural intrusion into usable space.
Column Grid and Layout Planning
Column spacing affects both structural efficiency and operational layout. An optimized column grid aligns with racking modules and traffic lanes, reducing wasted space and improving storage density.
Design principles include:
- Aligning columns with racking row ends
- Avoiding column interference in main aisles
- Balancing bay spacing with structural economy
A well-planned grid enhances flexibility and simplifies future reconfiguration.
Roof and Wall System Performance
High-capacity warehouses require roof and wall systems that provide durability, thermal performance, and low maintenance.
Important design considerations include:
- Roof load capacity for equipment and maintenance access
- Daylighting integration to reduce energy consumption
- Insulated wall panels for temperature-sensitive goods
- Wind and seismic performance based on site conditions
Steel cladding systems can be customized to meet both structural and environmental requirements.
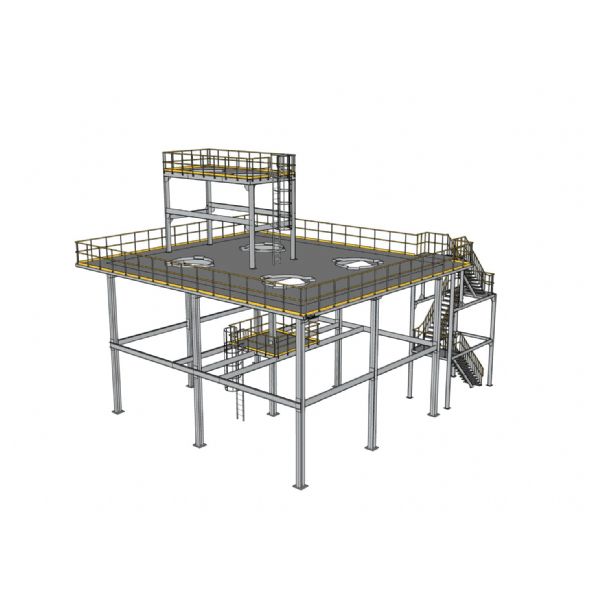
Integration with Material Handling Systems
Modern warehouses rely heavily on material handling technology. Structural design must accommodate:
- Conveyor systems and suspended equipment
- Automated storage and retrieval systems
- Mezzanine platforms or pick modules
Early coordination ensures that loads from equipment are properly supported and integrated into the steel structure.
Fire Safety and Code Compliance
High storage density increases fire risk, making fire protection a critical design aspect. Steel warehouse design must comply with applicable fire codes and standards, including:
- Fire-resistant coatings or protection systems
- Sprinkler system clearance requirements
- Smoke ventilation and compartmentation
Fire safety requirements often influence clear height, column spacing, and roof design.
Flexibility and Future Expansion
A key advantage of steel construction is adaptability. High-capacity warehouses should be designed with future growth in mind.
Future-proofing strategies include:
- Allowing for racking load increases
- Designing end walls for horizontal expansion
- Providing reserve capacity in foundations and frames
This approach reduces long-term capital expenditure and extends building service life.
Cost Efficiency Through Integrated Design
Effective high capacity steel warehouse design balances performance with cost efficiency. Integrated design strategies focus on:
- Optimized steel tonnage
- Standardized components
- Efficient fabrication and erection methods
Collaboration between designers, fabricators, and operators leads to better cost control and predictable project outcomes.
Choosing the Right Structural Solution
Selecting an experienced steel structure warehouse solution provider ensures that design principles are translated into reliable, buildable structures. Proven expertise in high-load applications and large-span steel systems significantly reduces project risk.
Conclusion: Designing Warehouses for Maximum Capacity and Performance
High-capacity steel warehouses are engineered systems where structure, storage, and operations must work together seamlessly. By focusing on span width, racking load, vertical utilization, and future flexibility, project stakeholders can create warehouse facilities that support high throughput, operational efficiency, and long-term value.
A disciplined approach to high capacity steel warehouse design ensures that warehouses are not only larger, but smarter, safer, and more adaptable to evolving logistics demands.






